Applies to: Dental machines
Milling titanium
How to mill non-precious metals? How to mill titanium?
Introduction
Machining non-precious metals requires special attention to a few items if you want to achieve perfect results.
- The collet chuck of the spindle needs to be tightened firmly, otherwise the tool will be pressed into the collet chuck.
- The collet chuck of the spindle needs to be clean and without grease inside, otherwise rotational imperfections during machining will degrade the machining results and can cause tool breakages.
- The .stl-file must be free from design errors .
To be on the safe side, we strongly recommend to do the following:
- Activate the option in DentalCAM.
- Add at least 1 backup tool to the tool magazine in case of a tool breakage.
For milling titanium on a S1 or S2 construction year <2016 with a wet grinding module, a flow sensor needs to be retrofitted (see Quick reference guidesS1). After installing the flow sensor, you need to unlock your abutment holder as extra equipment. The activation code is sent to you together with the abutment holder.
vhf machines suitable for milling titanium
| Machine | Wet /dry machining | Material | Supported holder |
|---|---|---|---|
|
N4 / N4+ |
Wet machining |
Prefabricated abutments |
Abutment holder:
|
|
R5 |
Wet machining |
|
Abutment holder:
|
|
S1 |
with wet grinding module: Wet machining |
Discs and prefabricated abutments |
Abutment holder:
|
|
S2 / S5 |
with wet grinding module: Wet machining |
Discs and prefabricated abutments |
Abutment holder:
|
|
Z4 |
Wet machining |
Prefabricated abutments |
Abutment holder:
|
Tools for machining titanium
| Match code (4-axis except E4) | Match code (5-axis) | Cutting edge diameter | Tool geometry | Teeth | DentalCAM 7 | DentalCAM 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
M060–R2-32 |
M060–R2–35 |
0.6 mm |
Radius |
2 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
M100–R2-32 |
M100–R2–35 |
1.00 mm |
Radius |
2 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
M120–T2–32 |
M120–T2–35 |
1.20 mm |
Torus |
2 |
Yes |
Yes |
|
M200–R4–32(-C)* |
M200–R4–35(-C)* |
2.00 mm |
Radius |
4 |
Yes |
Yes |
We highly recommend the use of original vhf tools for optimal results and a high service life of your machine and its components.
Indications that can be machined
The table shows all indications that can be machined from
| Indication | N4 / N4+ | R5 | S1 | S2 / S5 | Z4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Coping and bridge framework |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Fully anatomical crown/bridge |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Abutment |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Telescope crown |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Implant bar |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Secondary crown |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
|
Occlusal screw-retained bridge |
No |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Tool life
The maximum values for tool service life that you can actually achieve with your tools depend on many factors, such as the quality of the tools, the quality of the blanks, machine maintenance and cleaning, etc.
The tool life depends on the bending strength of the processed material. Different bending strengths result in different tool life.
We highly recommend the use of cooling lubricant for optimized results and tool life.
| Material | Tool life |
|---|---|
|
Titanium discs with cooling lubricant |
approx. 6 hours |
|
Titanium prefabricated abutments with cooling lubricant Tec Liquid Pro without cooling lubricant Tec Liquid Pro |
5 – 10 hours (approx. 10 – 20 blanks) 2 hours (approx. 4 blanks) |
Correct setting of bars
Positioning bars in X- and Y-direction
| Correct | Incorrect | Description |
|---|---|---|
|
|
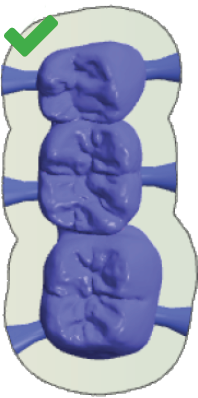
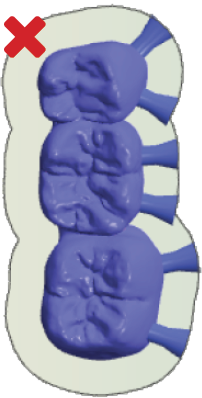
Place bars evenly on all sides If you place bars on only one side, vibration during machining may occur. This can lead to the blank or tool getting damaged. Correct (left): Bars on all sides of the object Incorrect (right): Bars on only one side of the object |
|
|
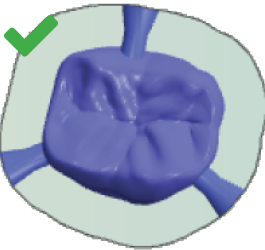
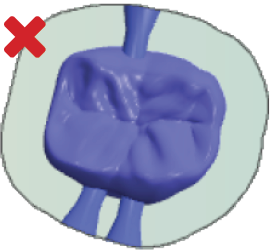
Place bars with sufficient distance from each other If there isn't enough space between bars, the air nozzle of the spindle may not be able to blow off machining debris as required, which can damage the tool. Correct (left): Bars with suitable distances between them Incorrect (right): Bars without suitable distances between them |

|
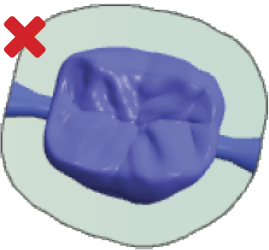
|
Set enough bars You should at least set 3 bars for each object. Multi-unit-objects generally require 2 bars per unit. Otherwise, vibrations may occur during machining, which can lead to the blank or tool getting damaged. Correct (left): Enough bars have been set Incorrect (right): Too few bars have been set |
Positioning bars in Z-direction
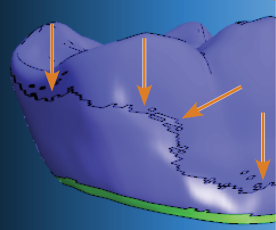
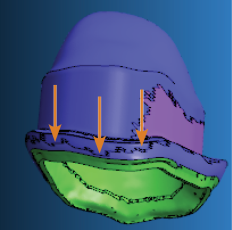
- Position all bars on the equator. If the equator is on the prepline, position the bar approx. 1 mm above the equator.
You need to position all bars completely on the object.
The bar in the figure below is positioned too high. Only a part of the bar is positioned on the object.
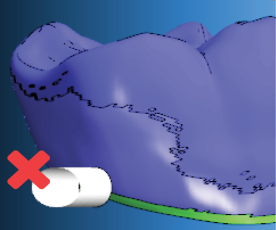
The bar in the figure below is positioned too low. Only a part of the bar is positioned on the object. Additionally, the bar is positioned on the prepline.
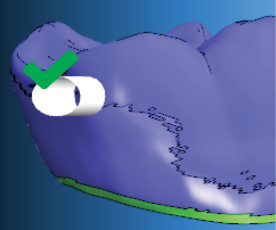
The bar in the figure below is correctly positioned on the equator.